Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) cause 17.9 million deaths each year, with 80% attributed to heart attacks and strokes (WHO). Yet, diet is one of the most controllable risk factors. Embracing a plant-based diet for heart health offers an evidence-backed strategy for preventing and even reversing heart disease.
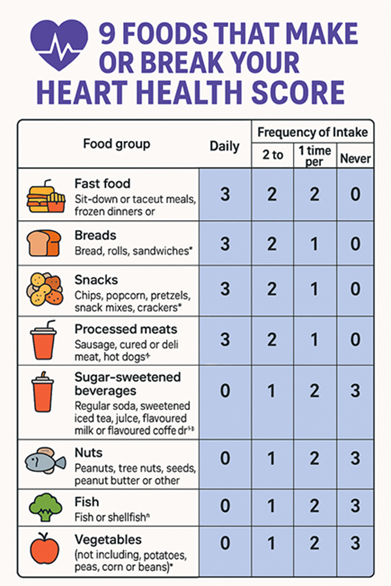
Types:
- Vegan diet for heart health: Excludes all animal products.
- Vegetarian diet and heart health: Allows dairy and eggs.
- Whole food plant-based diet for heart health: Focuses on unprocessed plant foods.
🌱 Key Takeaway: The American Heart Association states that plant-based diets can reduce cardiovascular mortality by 32% (AHA).
Resource: JACC: Fiber Intake
How a Plant-Based Diet Supports Heart Health
A plant-based diet for heart health promotes cardiovascular wellness through multiple mechanisms:
- Lowers LDL cholesterol: Soluble fibers from oats and beans help reduce “bad” cholesterol.
- Reduces blood pressure: Potassium-rich foods like spinach and bananas regulate hypertension.
- Decreases inflammation: Phytochemicals in plants combat vascular inflammation.
- Improves arterial function: Enhances blood vessel elasticity and reduces plaque buildup.
Research also validates that a plant-based diet for lower blood pressure and cholesterol management is effective in prevention and treatment scenarios (PCRM).
Resource: The Lancet: Plant-Based Diet
Best Plant-Based Foods for Heart Health
Here are the top heart-smart plant-based foods:
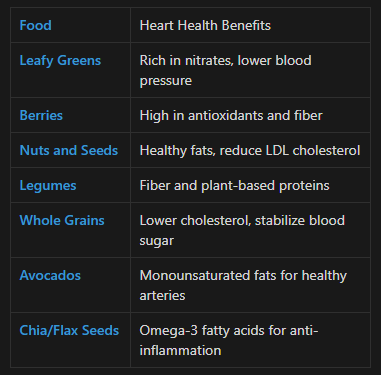
“Just two questions predict heart risk: How many vegetables do you eat daily? Do you drink sugary beverages?” (Johnston et al., 2020)
Many plant-based staples like walnuts and berries also [combat inflammation], doubling your protection.
Heart Disease Prevention with Plant-Based Diet
A plant-based diet and heart disease are closely linked:
- Processed Meats & Sugary Drinks: Associated with highest cardiovascular risk (Micha et al., 2017).
- Plant-Based Pillars: Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds correlate with significantly lower risks.
- Eliminate High-Risk Foods: Reduce fast food, refined grains, processed meats, and sugary beverages.
🌍 WHO Finding: Low fruit and vegetable intake causes over 2 million CVD deaths yearly (WHO).
Tips for Transitioning to a Heart-Healthy Plant-Based Diet
- Swap Processed for Whole: Replace processed meats with lentils or tofu.
- Prioritize Fruits and Veggies: Fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables.
- Nuts and Seeds Power: Include them at least four times a week.
- Smart Snacks: Choose spiced nuts or roasted chickpeas over salty snacks.
- Use Herbs, Not Salt: Flavor foods naturally with herbs, spices, and citrus.
- Balanced Meals: Ensure meals include fiber, protein, and healthy fats.
💡 Pro Tip: Use budget-friendly swaps like frozen vegetables and bulk legumes.
Sample Plant-Based Heart-Healthy Meal Plan
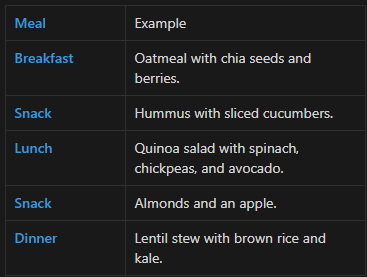
This plan not only helps in lowering cholesterol but also reduces blood pressure naturally.
A heart-healthy diet also [supports brain function], creating a wellness domino effect.
Yes, research supports that a plant-based diet for heart health can significantly reverse coronary artery disease (AHA).
Blood pressure and cholesterol improvements may be seen in just 3–6 weeks.
While fish provides omega-3s, nuts and seeds like walnuts and flaxseed are excellent plant-based alternatives.
Include legumes, quinoa, tofu, and tempeh—plenty of protein without the cholesterol.
Soluble fiber is crucial—it binds LDL cholesterol and promotes heart health.
Conclusion
Shifting to a plant-based diet for heart health is more than a trend—it’s a proven, science-backed lifestyle change that could dramatically reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease. By focusing on plant-based foods for heart health, eliminating high-risk processed foods, and embracing whole, nutrient-dense plants, you’re choosing a healthier future.
❤️ Closing Fact: Switching to plant-based foods could prevent 1 in 5 premature CVD deaths.